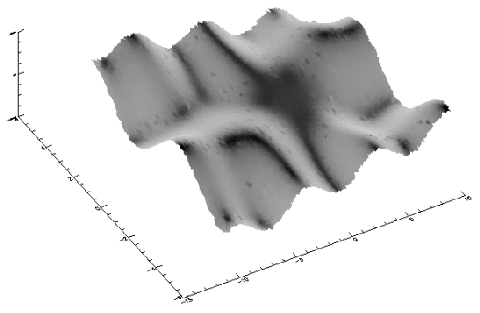
A two-dimensional array containing the values that make up the surface. If x and y are supplied, the surface is plotted as a function of the X,Y locations specified by their contents. Otherwise, the surface is generated as a function of the array index of each element of z.
A two-dimensional array containing the values that make up the surface. If x and y are supplied, the surface is plotted as a function of the X,Y locations specified by their contents. Otherwise, the surface is generated as a function of the array index of each element of z.x
 A two-dimensional array specifying the x-coordinates for the contour surface. Each element of x specifies the x-coordinate of the corresponding point in z (xij specifies the x-coordinate for zij).
A two-dimensional array specifying the x-coordinates for the contour surface. Each element of x specifies the x-coordinate of the corresponding point in z (xij specifies the x-coordinate for zij).y
 A two-dimensional array specifying the y-coordinates for each elevation. Each element of y specifies the y-coordinate of the corresponding point in z (yij specifies the y-coordinate for zij).
A two-dimensional array specifying the y-coordinates for each elevation. Each element of y specifies the y-coordinate of the corresponding point in z (yij specifies the y-coordinate for zij).